Everything You Need to Know About OBESITY

Table of contents
- What is obesity?
- What are the symptoms of obesity?
- Why does obesity happen/ causes/ factors?
- Classification of obesity?
- What is BMI?
- How to diagnose obesity?
- How to diagnose obesity-related health risks?
- What are the associated chronic disorders of obesity?
- How can be obesity treated?
- Which drugs are prescribed for weight loss?
- Weight loss surgery and types?
- How to prevent obesity?
In today’s fast-paced world, many of us find ourselves battling an ever-increasing foe: Obesity
What exactly is obesity?
It’s mainly our body’s extra fat that has been accumulated due to consuming excess amounts of calories that we need to propel our body daily.
Understanding the enemy/obesity:
Our body works like a machine. As we know, excess fuel does nothing beneficial; meanwhile, it has some adverse effects on that machine, just as it does on our bodies. We should consume an adequate amount of calories that we need to work our bodies properly. Taking in excess amounts of calories results in the accumulation of fat in our bodies, which leads to obesity over time.
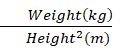
What are the symptoms of obesity?
Typically, there are no particular symptoms of obesity. There are some measurements by which we can predict the prevalence:
- BMI > 25
- Excess body mass (% of fat)
- A waist circumference greater than 40 inches in men and more than 35 inches in women
- Android vs. Gynoid Fat Distribution
What is Android?
Android can be defined as having a fat distribution around the midsection or waist (belly button).
What is a gynoid?
Gynoid refers to the area of the hips that is located at the tops of the thighs.
Why does obesity happen? Factors that influence obesity?
Obesity is a complex condition that can be influenced by numerous variables. The following are a few of the key contributors:
Diet:
Obesity is mostly caused by the kinds of meals we eat and the way we eat. Eating low-nutrient, high-calorie foods like processed meals, sugary snacks, and fast food can cause weight gain.
Physical activity:
Inadequate physical activity is another main reason for obesity. Leading sedentary lifestyles as a result of desk work, screen time, and inactivity, means people aren’t burning enough calories to stay at a healthy weight.
Genetics:
Genetics can influence a person’s susceptibility to obesity. Even in cases where they eat a very healthy diet and exercise frequently, some people may be genetically predisposed to gain weight.
Psychological Factors:
Overeating or unhealthy eating habits can result from emotional variables such as stress, depression, anxiety, and trauma. These circumstances can also cause people to turn to food as a coping mechanism or source of comfort.
Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions and drugs can contribute to weight gain and obesity. These include illnesses that restrict movement or physical activity, mental drugs, and hormonal disorders (e.g., hypothyroidism and polycystic ovarian syndrome).
Environment:
Our surroundings can promote unhealthy behaviors that contribute to obesity. Variables such as easy access to unhealthy foods, food marketing, socioeconomic status, cultural norms, and neighborhood safety can all influence dietary choices and physical activity levels.
Sleep:
Poor sleep patterns, including insufficient sleep or having sleep disorders like sleep apnea, can disrupt hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism, potentially leading to weight gain and obesity.
Social and Economic Factors:
Obesity rates can be influenced by socioeconomic variables, including education, income level, and access to healthcare.
Classification of overweight/ obesity:
Classification | BMI(kg/m2) |
| Underweight | <18.5 |
| Normal | 18.5-24.9 |
| Overweight | 25-29.9 |
| Obesity, class 1 | 30-34.9 |
| Obesity, class 2 | 35-39.9 |
| Obesity, class 3 | >40 |
Obesity is mainly classified based on BMI (Body Mass Index). To understand the classification of obesity you need to know about BMI.
What is BMI?
BMI(Body Mass Index) is a measurement that can be calculated by dividing a person’s body weight in kilograms by their square of height in meters.
The BMI equation is given below:
BMI =
You can calculate your Body Mass Index from this equation and determine which category you fall into.
How to diagnose obesity?
Body mass index (BMI) gives us the option to diagnose a person’s obesity concerning their height.
There are some other fat measurement tests which are more accurate:
- Waist-to-hip measurements
- Measuring skinfold thickness
- Dual-energy radiographic absorptiometry (DEXA) scans
- Screening examinations, including MRI, CT, and Ultrasound scans
How to diagnose obesity-related health risks?
A doctor can do some particular tests like –
- Blood sugar level
- Blood cholesterol level
- Liver function test
- Thyroid screening
- Diabetes screening
- Cardiac tests(ECHO, ECG)
What are the associated chronic disorders of obesity?
Researchers have found a direct link with the following health conditions:
- Heart disease
- Type 2 diabetes
- Hypertension
- Stroke
- Gallbladder disease
- Sleep apnea
- Certain cancers (Most commonly colorectal cancer among men and breast cancer among women)
- Osteoarthritis
- Fatty liver disease
- Poor wound healing
How can be obesity treated?
There are mainly two ways to treat obesity. The first one is Medical Management. Such as –
Lifestyle modification
Here are some tips about lifestyle modification:
- Increase physical activity or exercise.
- Eat only sitting down at one place.
- Leave the table as soon as eating is done.
- Don’t combine eating with other activities, such as reading or watching television.
- Don’t put bowls of food on the table.
- Stock home with healthier food choices.
- Keep all food in cupboards where it can’t be seen.
- Shop for groceries from a list after a full meal.
- Limit the amount of money taken when shopping.
- Plan meals and snacks.
- Plan for special events, parties, and dinners.
- Immediately place leftovers in storage container and refrigerate or freeze them for another meal.
- Negotiate with family to eat healthier food.
- Snack on fresh vegetables and fruits.
Psychological support
Make a positive mindset about your health and build a psychology that neither you are going to overeat nor you are going to consume any unhealthy food.
Some tips about psychological support:
- Eat slowly and savor each mouthful.
- Put down the fork between bites.
- Delay eating for 2 to 3 min and converse with others.
- Postpone a desired snack for 10 min.
- Serve food on a smaller plate.
- Leave 1 or 2 bites of food on the plate.
- Divide portions in half so that another portion can be permitted.
Drug
Which drugs are prescribed for weight loss?
One should go for the prescribed medication if the lifestyle modification and psychological support didn’t work for them. These medications either prevent the absorption of fat or suppress appetite.
Medications approved to treat obesity:
- Orlistat(Xenical)
- Phentermine-topiramate(Qsymia)
- Naltrexone-bupropion(Contrave)
- Liraglutide(Saxenda)
- Semaglutide(Wegovy)
- Stemelanotide(IMCIVREE)
[N.B: Don’t use them without consulting with your doctor. These medications should use after your complete body checkup to understand that which one will work on you better and you don’t face any complications.]
Surgery
What is weight loss surgery?
Weight loss surgery is also known as bariatric surgery. In this surgery, the stomach is cut down to a smaller size than before so that it feels fuller sooner, and one should end up eating less food.
Who should go for the weight loss surgery?
If one’s Body Mass Index (BMI) is 40 or greater than that, additionally suffering from chronic health conditions associated with obesity and tried to lose weight by diet, exercise and medicine but didn’t work out so well, then those individuals should go for surgery.
What are the types of weight loss surgery?
In the United States, the sergeons mainly perform 4 types of surgery for weight loss:
- Gastric sleeve – In this procedure removes most of your stomach.
- Gastric bypass – In this procedure staples your stomach to create two sections and add them to the small intestine.
- Adjustable gastric band – In this procedure doctor places a ring with an inner inflatable band around the top of your stomach.
- Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch – It is mainly the mixture of gastric sleeve and gastric bypass surgery.
The second treatment for obesity or weight loss is the Nutritional Management. Such as –
- Food choice changes
- Nutrition education
- Maintain micronutrient intake
How to prevent obesity?
Weight loss programs should combine a nutritionally balanced dietary regimen with exercise and lifestyle modification at the least possible expense. Selecting the appropriate treatment strategy depends on the goals as well as your health risks. Prevention options include the following:
- A low-calorie diet, increased physical activity, and lifestyle modifications.
- The preceding plus pharmacotherapy.
- Surgery plus an individually prescribed dietary regimen, physical activity, and lifestyle modification program.
- Prevention of weight gain through energy balance.
Takeaway:
Obesity is a chronic disease and heart problems and type-2 diabetes are the main health conditions developing due to obesity in the human body.
Some healthy eating habits and some lifestyle changes can reverse this condition.
It’s not just about shedding pounds; it’s about fostering a culture of wellness and empowerment. Together, let’s take a stand against obesity and embrace healthier, happier lives.
100% FREE SUBSCRIPTION
What content would you like to receive?